Simplified services for application exposition
Context
Kubernetes runs its pods internally. By default, a pod is not exposed outside the cluster. To publish an application to internet or to internal network, you should deal with DNS, TLS certificate and proxy configurations.
K8SaaS provides an all-in-one application publication service that help a developer to expose his application.
Features:
- scalable proxy
- DNS domain in kaas.thalesdigital.io
- Corresponding valid TLS certificate
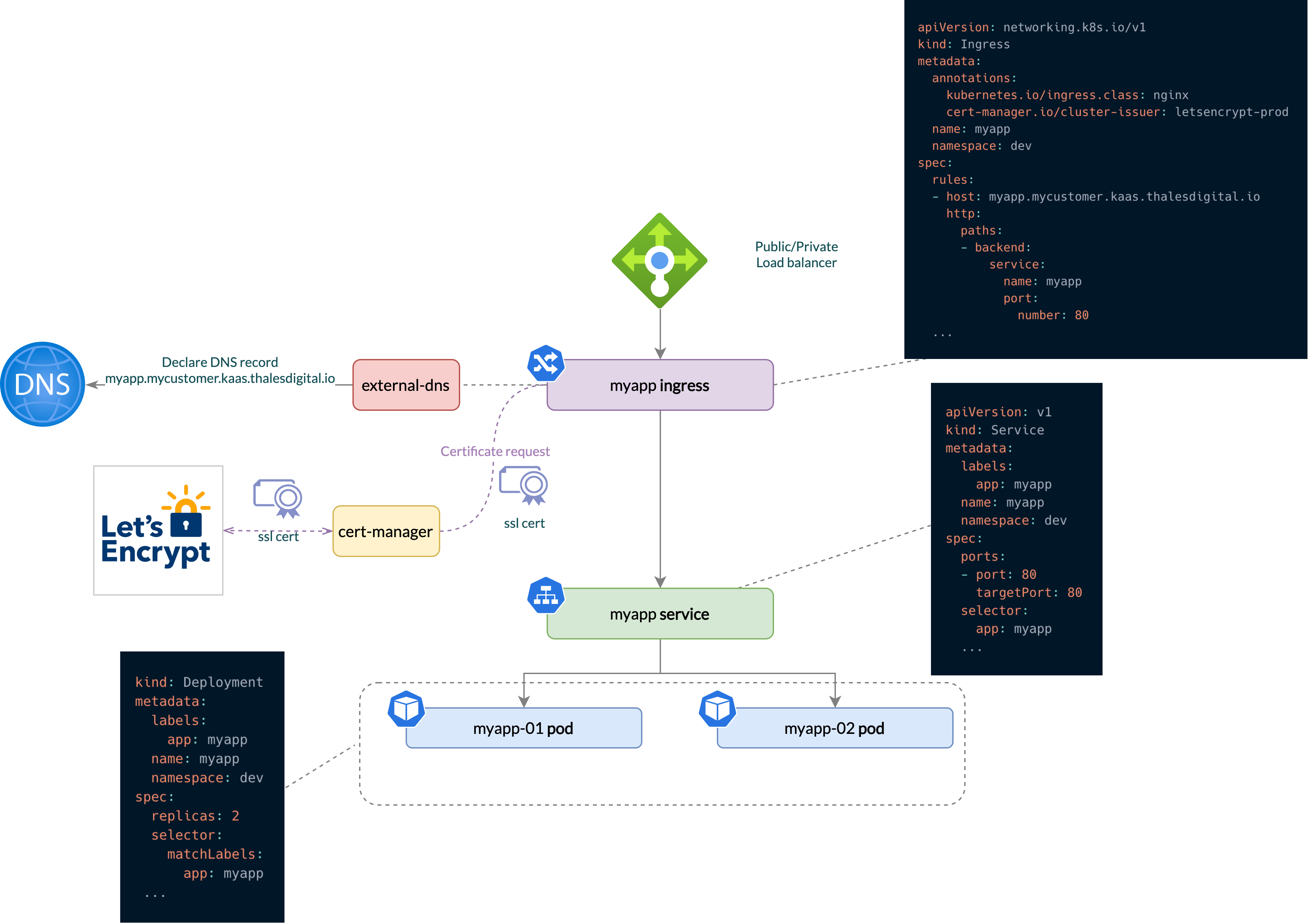
Use case
- Publish an application to internet securely
- Publish an application to the peered network only
- SSL passthrough
What to do ?
We assume you have a service called aks-helloworld-one exposed on TCP:80.
To expose its application, you have to create an ingress object.
Option 1 - using kubectl apply:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: <your_app>-ingress # ex: helloworld-ingress
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-staging # ex: see Usage
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx # ex: see Usage
tls:
- hosts:
- <your_app>.<your_cluster>.kaas.thalesdigital.io # ex: hello-world.dev.project.kaas.thalesdigital.io
secretName: <your_app>-<your_cluster>-tls # ex: helloworld-dev-tls, in most case this secrete should be unique.
rules:
- host: <your_app>.<your_cluster>.kaas.thalesdigital.io # ex: hello-world.dev.project.kaas.thalesdigital.io
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: aks-helloworld-one
port:
number: 80
Option 2 - using helm chart:
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx # ex: see Usage
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-staging # ex: see Usage
hosts:
- host: <your_app>.<your_cluster>.kaas.thalesdigital.io # ex: hello-world.dev.project.kaas.thalesdigital.io
paths: ["/"]
tls:
- secretName: <your_app>-<your_cluster>-tls # ex: helloworld-dev-tls, in most case this secrete should be unique.
hosts:
- <your_app>.<your_cluster>.kaas.thalesdigital.io # ex: hello-world.dev.project.kaas.thalesdigital.io
Explanations:
- metadata.name:
- spec.ingressClassName:
- to use the ingressClass respective to your ingress controller, if your controller is :
- internal (thales provided ip range): nginx-internal
- external (public, internet facing): nginx
- namespaced (deployed in a namespace, shared offer):
nginx-<your_namespace_name>
- to use the ingressClass respective to your ingress controller, if your controller is :
- metadata.annotation.cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer:
- for testing : letsencrypt-staging
- for prod : letsencrypt-prod
- spec:
- according to your application endpoint and service configuration
Once deployed, you should be able to list your application with:
kubectl get ingress -n NAMESPACE
Note: The TLS certificate generation should take 2 minutes. After 5min, if the configuration is not ready, you should have a look to the kubernetes events with:
kubectl get events -n NAMESPACE
Note: Send those logs to the support if needed
HOWTO
Use a valid certificate
When using letsencrypt-staging, if you try to connect with a browser to your ingress url, you'll see a "Untrusted/Wrong Certificate". It's a normal behavior. letsencrypt-staging provides a fake certificate in order to test the certificate provisioning before going to letsencrypt-prod.
To use a valid certificate, you should update the following line of your ingress:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-staging
by
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod
Then, apply the change to the cluster.
Note: We highly recommend testing against letsencrypt staging environment before using our production environment. This will allow you to get things right before issuing trusted certificates and reduce the chance of your running up against rate limits.
Bring your own certficate
In order to use your own certificate, you have to :
- Disable the letsenscrypt provider for your ingress
- Provide the certificate as a secret and indicate to nginx to use it
Disable letsencrypt provider
Remove all cert-manager.io/* annotations
Import your own certificate into the ingress
To allow Kubernetes to use the TLS certificate and private key for the ingress controller, you create and use a Secret. The secret is defined once, and uses the certificate and private key file. You then reference this secret when you define ingress routes.
The following example creates a Secret named your-ingress-tls in dev namespace:
kubectl create secret tls your-ingress-tls \
--namespace dev \
--key ingress-tls.key \
--cert ingress-tls.crt
Then indicate the ingress route to use this secret as a tls certificate (based on previous example):
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- <your_app>.<your_cluster>.kaas.thalesdigital.io # ex: hello-world.dev.project.kaas.thalesdigital.io
secretName: your-ingress-tls
Configure SSL-Passthrough
First, the nginx ingress controller need to be updated by the k8saas level 2 team. Please ask the support to enable this feature listing:
- your customer name
- your cluster name
Once done, you should be able to use the parameters:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTPS"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: "true"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
Configure permanent redirection
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: <your_app>-ingress # ex: helloworld-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/permanent-redirect: newurl # ex: newurl.kaas.thalesdigital.io
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod # ex: see Usage
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx # ex: see Usage
tls:
- hosts:
- <your_app>.<your_cluster>.kaas.thalesdigital.io # ex: oldurl.kaas.thalesdigital.io
secretName: <your_app>-<your_cluster>-tls # ex: helloworld-dev-tls, in most case this secrete should be unique.
rules:
- host: <your_app>.<your_cluster>.kaas.thalesdigital.io # ex: oldurl.kaas.thalesdigital.io
http:
paths:
- path: /
Configure a whitelist
Note: to perform a whitelisting properly, we strongly recommend using a firewall. Before setuping this feature, please have a look at Pre-Configured firewall section.
To enable the whitelisting feature, you just have to update your current ingress configuration using:
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/whitelist-source-range: 49.36.X.X/32
[...]